- 權威控制
1.翻譯:
2.釋義:
圖書資訊學中整理圖書館目錄和目錄資訊的方式,以達到書目控制。關於個人名稱、團體名稱、劃一題名、集叢題名、標題等標目形式的一致化及其維護,使同一主題使用相同、唯一的標題(獨特性),以辨識資源的匿名性、重複性、交替性,提供一致性資訊組織,做為編目者遵循依據,避免讀者誤檢(一名多人)、漏檢(一人多名)。這些標題貫徹整個目錄庫並能與其他交叉引用的資料庫協同工作。
In library science, authority control is a process that organizes bibliographic information.
圖書資訊學中組織書目資訊的程序
for example in library catalogs by using a single, distinct spelling of a name (heading) or a numeric identifier for each topic.
以圖書館目錄而言,每一主題使用唯一、可與他人區隔的名字或辨認碼。
這些具有獨特性的標題可指引讀者檢索到所有與主題相關的資訊
The word authority in authority control derives from the idea that the names of people, places, things, and concepts are authorized, i.e., they are established in one particular form.
權威控制中的詞彙衍生於經過授權、具有特定格式的人名、地名、事物、觀念
The unique header can guide users to all relevant information including related or collocated subjects.這些具有獨特性的標題可指引讀者檢索到所有與主題相關的資訊
These one-of-a-kind headings or identifiers are applied consistently throughout catalogs which make use of the respective authority file, and are applied for other methods of organizing data such as linkages and cross references.
This organization helps the library staff maintain the catalog and make it user-friendly親和力 for researchers.
3.舉例:
(1)筆名或化名
作家林良,筆名子敏,又被稱為小太陽。該館可訂定一致的題名,當讀者查檢作者林良時,即可檢索到所有林良的作品。
(2)繁簡體
臺灣的資料庫:讀者不論是以簡體或繁體查檢,皆可得到繁體的檢索結果
中國的資料庫:讀者僅能以繁體查檢,才能得到繁體的檢索結果,未做繁簡體轉換的權威控制
Take the subject of Princess Diana in Wikipedia for example:在維基百科中,以戴安娜王妃作為主題舉例
In an online library catalog, various entries might look like the following:
在圖書館線上目錄中,可能有下列不同的款目形式:
- Diana. (1)
- Diana, Princess of Wales. (1)
- Diana, Princess of Wales, 1961-1997 (13)
- Diana, Princess of Wales 1961-1997 (1)
- Diana, Princess of Wales, 1961-1997 (2)
- DIANA, PRINCESS OF WALES, 1961-1997. (1)
- Diana, Princess of Wales, - Iconography. (2)
這些不同的詞彙描述相同的人,因此,將這些標題做權威控制,形成唯一、獨特的檢索款目或權威標題,有時候被命名為檢索點:(通常是常用寫法)
Diana, Princess of Wales, 1961-1997
Princess Diana is described in one authority file as "Windsor, Diana, Princess of Wales" which is an official heading.在權威檔中,以"威爾斯王妃黛安娜"描述戴安娜王妃
檢索結果如下:
There is a page named "Diana, Princess of Wales" on Wikipedia
註:辨認同名同姓:
(1)出生死亡年(2)身分證字號或其他識別碼
4.權威紀錄(Authority Record):
將每一經由權威控制的標題組合而得的一筆紀錄資料。
權威資料是一種控制的檢索項(controlled access point)。
5.權威檔(Authority File)
將權威紀錄匯集並併入一個資料庫中而形成,方便館員統一管理,維護更新文件以及其間的「邏輯關係」。
權威資料是一種控制的檢索項(controlled access point)。
5.權威檔(Authority File)
將權威紀錄匯集並併入一個資料庫中而形成,方便館員統一管理,維護更新文件以及其間的「邏輯關係」。
Authority records can be combined into a database and called an authority file.
reference:
wiki(維基)
- 權威資料功能需求
英文:Functional Requirements for Authority Data,簡稱FRAD
歷史:
其最終報告(Final Report)由國際圖聯權威紀錄的功能需求與編號工作組(IFLA Working Group on Functional Requirements and Numbering of Authority Records,簡稱FRANAR)於2008年12月完成,直到2009年4月,被國際圖聯常務委員會編目組(Standing Committee of the IFLA Section on Cataloguing)和國際圖聯分類索引組(IFLA Classification and Indexing)認可通過,後於2013年7月補充(不夠完整)、修訂(原本有誤)。
註:由於IFLA FRBR研究小組認為有必要擴展FRBR模式涵蓋權威資料,國際圖聯書目控制部(IFLA Division of Bibliographic Control)和國際圖聯世界書目控制與國際機讀編目格式計畫(IFLA Universal Bibliographic Control and International MARC Programme,簡稱UBCIM)於1999年4月成立權威紀錄的功能需求與編號工作組(The Working Group on Functional Requirements and Numbering of Authority Records ,簡稱FRANAR)。2003年,UBCIM計畫解散(任務結束),改由國際圖聯-國家圖書館館長會議 書目標準聯盟(IFLA-CDNL Alliance for Bibliographic Standards ,簡稱ICABS) 接手,並與英國國家圖書館共同負責FRANAR
註:國家圖書館館長會議:Conference of Directors of National Libraries,簡稱CDNL
註:FRANAR朝下列三個方向運作(三項任務):
註:國際標準化組織情報文獻工作技術委員會(ISO/TC46):ISO Technical Committee 46
→與圖書館最直接相關的委員會
Standards developed under the ISO Technical Committee on Information and Documentation are focused on facilitating access to knowledge information and developing appropriate automated tools, computer systems and services to obtain the information owned by libraries, archives, museums and similar enterprises.
Scope:
Standardization of practices relating to libraries, documentation and information centres, publishing, archives, records management, museum documentation, indexing and abstracting services, and information science.
reference:
http://www.niso.org/international/2014_tc46_meeting/TC46_work/
http://www.iso.org/iso/iso_technical_committee?commid=48750
實現的三項職能:
目次、內容(content):
考試重點!!!
研究目的:概念模型的設計用途
歷史:
其最終報告(Final Report)由國際圖聯權威紀錄的功能需求與編號工作組(IFLA Working Group on Functional Requirements and Numbering of Authority Records,簡稱FRANAR)於2008年12月完成,直到2009年4月,被國際圖聯常務委員會編目組(Standing Committee of the IFLA Section on Cataloguing)和國際圖聯分類索引組(IFLA Classification and Indexing)認可通過,後於2013年7月補充(不夠完整)、修訂(原本有誤)。
註:由於IFLA FRBR研究小組認為有必要擴展FRBR模式涵蓋權威資料,國際圖聯書目控制部(IFLA Division of Bibliographic Control)和國際圖聯世界書目控制與國際機讀編目格式計畫(IFLA Universal Bibliographic Control and International MARC Programme,簡稱UBCIM)於1999年4月成立權威紀錄的功能需求與編號工作組(The Working Group on Functional Requirements and Numbering of Authority Records ,簡稱FRANAR)。2003年,UBCIM計畫解散(任務結束),改由國際圖聯-國家圖書館館長會議 書目標準聯盟(IFLA-CDNL Alliance for Bibliographic Standards ,簡稱ICABS) 接手,並與英國國家圖書館共同負責FRANAR
註:國家圖書館館長會議:Conference of Directors of National Libraries,簡稱CDNL
註:FRANAR朝下列三個方向運作(三項任務):
- 定義、確定權威紀錄的功能需求,延續FRBR工作
- 研究國際標準權威記錄號碼(International Standard Authority Data Number,簡稱ISADN)的可能性
- 擔任IFLA與其他權威檔相關機構的協調單位、來往窗口,與之一起工作
註:國際標準化組織情報文獻工作技術委員會(ISO/TC46):ISO Technical Committee 46
→與圖書館最直接相關的委員會
Standards developed under the ISO Technical Committee on Information and Documentation are focused on facilitating access to knowledge information and developing appropriate automated tools, computer systems and services to obtain the information owned by libraries, archives, museums and similar enterprises.
Scope:
Standardization of practices relating to libraries, documentation and information centres, publishing, archives, records management, museum documentation, indexing and abstracting services, and information science.
共有114個國際標準與ISO/TC46委員會有關
ISO/TC46委員會共做出32個ISO標準
37個參與國
33個觀察國
reference:
http://www.niso.org/international/2014_tc46_meeting/TC46_work/
http://www.iso.org/iso/iso_technical_committee?commid=48750
實現的三項職能:
- 從FRANAR工作組的角度,實現部分FRBR模型的延伸(extension)(外在,例如:擴建校區)和擴充(expansion)(內部,例如:增設一個學系)
- 處理編號,闡明權威資料識別碼或標準號碼的功能。每一筆控制資料皆有一個國際編號。例如:同名同姓可以學號識別身分
- 與其他單位聯繫,作為IFLA的來往窗口
目次、內容(content):
- Purpose研究目的
- Scope研究範圍
- Entity-Relationship Diagram and Definitions實體-關係圖與定義 (研究方法)
- Attributes屬性
- Relationships關係
- User Tasks使用者任務
考試重點!!!
研究目的:概念模型的設計用途
The conceptual model has been designed to:
- 提供一個明確定義、結構化的參考框架,使權威紀錄創建者製作的資料與使用者需求產生關聯,以評估功能需求,迎合紀錄使用者的需求Provide a clearly defined, structured frame of reference for relating the data that are
recorded by authority record creators to the needs of the users of that data. - 協助圖書館界及各界評估權威資料國際共享共用的潛在可能性 (全球視野)
Assist in an assessment of the potential for international sharing and use of authority data both within the library sector and beyond.
資訊管理機構:
人類的記憶存放於圖書館(library)、博物館(museum)、檔案館(archive),並由這些機構管理,是人類知識的呈現。其目錄是一系列經過組織的資料,用來描述資訊內容,而權威控制僅能處理置放於這些機構中的資料。
人類的記憶存放於圖書館(library)、博物館(museum)、檔案館(archive),並由這些機構管理,是人類知識的呈現。其目錄是一系列經過組織的資料,用來描述資訊內容,而權威控制僅能處理置放於這些機構中的資料。
使用者研究範圍:
- 建立、維護權威資料的資訊工作者;權威資料的創建者、維護者
authority data creators who create and maintain authority data. - 可能直接獲取權威資料或在圖書館目錄、國家書目等中間接透過受控檢索點和參照結構使用權威資料的終端使用者end users who use authority information either through direct access to authority data or indirectly through the controlled access points and reference structures in library catalogues, national bibliographies, etc.
權威資料定義:
關於個人、家族、團體、作品名稱資訊的集合體。這些名稱作為書目紀錄受控檢索點的基礎,當成近用的檢索項。
Authority data is defined as the aggregate of information about a person, family, corporate body, or work whose name is used as the basis for a controlled access point for bibliographic citations or for records in a library catalogue or bibliographic database.
研究方法:Entity-Relationship Methodology實體-關係方法論
(1)實體v.s.屬性:將某一事物定義為一項屬性還是一個獨立實體是設計概念模型的關鍵
FRBR模型的設計者認為,為了與模型中的其它實體關聯,將個人、團體定義為實體更適用。
這些實體的名稱可在權威紀錄中得到控制,並根據需要與其他權威紀錄、書目紀錄或館藏記錄產生關聯。
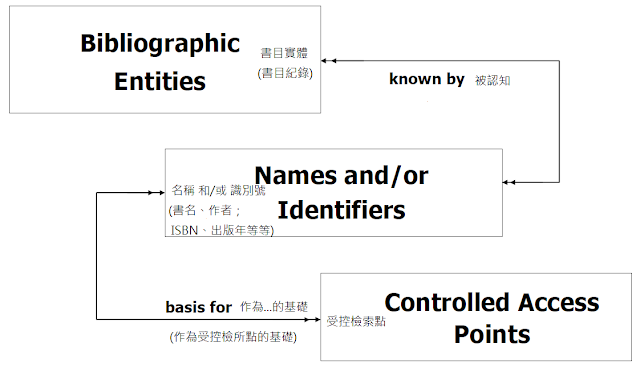
(2)Fundamental Basis for the Conceptual Model概念模型的基本原則:
註:關係均為雙箭頭、多對多
(3)Conceptual Model for Authority Data權威資料的概念模型:
將書目實體分為三組:
註:基於研究目的,此研究僅處理作者(name)、書名(title)的實體
(目錄中的主題也存在於權威控制的其他實體)
註:一人有多個識別號;一個識別號只對應至一人
註:人名代表對一個人的期望,可能實現或不會實現
註:圖例釋義:
實線矩形:一個實體,即權威資料使用者感興趣的一個對象
虛線矩形:包含二個以上的實體 (將幾個實體框在一起)
箭頭表示關係
單箭頭:起始端代表某一給定實體的事例,末端所指為一個實體的事例→ 一對一
雙箭頭:起始端代表某一給定實體的事例,末端所指為一個或多個實體的事例→ 一對多
註:出去是雙箭頭,回來也是雙箭頭→多對多
(1)實體v.s.屬性:將某一事物定義為一項屬性還是一個獨立實體是設計概念模型的關鍵
FRBR模型的設計者認為,為了與模型中的其它實體關聯,將個人、團體定義為實體更適用。
①在正式名稱時具有更好的靈活性FRBR 將此二者視為實體而非屬性的做法被保留在權威資料的概念模型中。
②去除將其表示為屬性時常出現的資料冗餘性問題
這些實體的名稱可在權威紀錄中得到控制,並根據需要與其他權威紀錄、書目紀錄或館藏記錄產生關聯。
(2)Fundamental Basis for the Conceptual Model概念模型的基本原則:
註:關係均為雙箭頭、多對多
(3)Conceptual Model for Authority Data權威資料的概念模型:
將書目實體分為三組:
①個人(person)、家族(family)、團體(corporate body)
②作品、內容表達、載體表現、單件
③概念(concept)、對象(object)、事件(event)、地點(place)→主題 不處理
註:基於研究目的,此研究僅處理作者(name)、書名(title)的實體
(目錄中的主題也存在於權威控制的其他實體)
註:一人有多個識別號;一個識別號只對應至一人
註:人名代表對一個人的期望,可能實現或不會實現
註:圖例釋義:
實線矩形:一個實體,即權威資料使用者感興趣的一個對象
虛線矩形:包含二個以上的實體 (將幾個實體框在一起)
箭頭表示關係
單箭頭:起始端代表某一給定實體的事例,末端所指為一個實體的事例→ 一對一
雙箭頭:起始端代表某一給定實體的事例,末端所指為一個或多個實體的事例→ 一對多
註:出去是雙箭頭,回來也是雙箭頭→多對多
reference:
IFLA
IFLA
註:維基百科列印文件的方法:
英文:Print/export-Download as PDF→Download the file
中文:列印(P).../Ctrl+P→變更→另存為PDF
註:維基百科的中文資料最少



沒有留言:
張貼留言